Intelligent Peak Deconvolution Analysis (i-PDeA II)
What Is i-PDeA? – An Introduction Through Application Examples
Intelligent Peak Deconvolution Analysis (i-PDeA) is a data analysis technique that extracts a single peak from co-eluted peaks and quantitates it by exploiting the differences in spectra between each compound.
i-PDeA II enables users to visualize and detect a minor single impurity even when the impurity is co-eluted with an analyte. It also facilitates the separation of hard-to-separate peaks on the column through computer processing and deconvolution of the spectrum information, which reduces the effort required to investigate separation parameters.
The following highlights some benefits of i-PDeA II through application examples.
Example 1: I have developed an ultrafast analysis method, but want to further reduce analysis time. However, shortening the analysis time would affect separation.
When you apply i-PDeA, you can selectively visualize only the components you want to view, even peaks that are not separated!
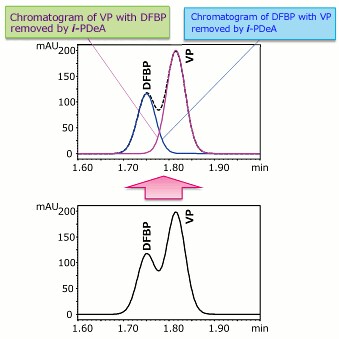
Using i-PDeA, the VP and DFBP Peaks Can Be Separated! (DFBP: Difluorobenzophenone, VP: Valerophenone)
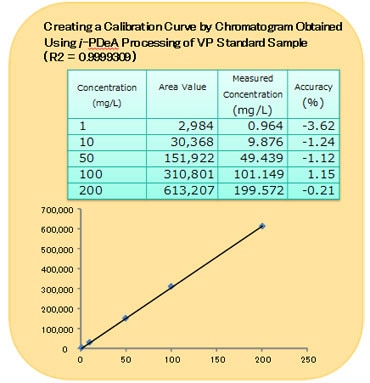
A Calibration Curve Created Using i-PDeA for the VP Standard Sample
Example 2: I want to correctly quantify the impurities that are eluted in the tailing of the main component peak.
With i-PDeA, no additional consideration of separation conditions is required! Quantitative calculation can be done directly!
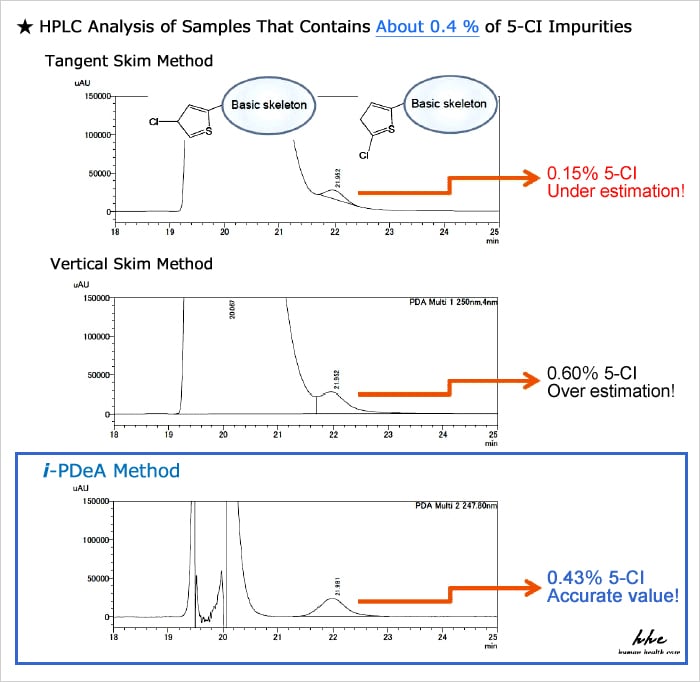
These materials were provided by Mr. Kanta Horie, Global Formulation Research, Pharmaceutical Science & Technology, Eisai Co., Ltd.
Compared to existing peak integration methods such as tailing (tangent skim method) and vertical separation (vertical skim method), i-PDeA permits quantitative calculation of impurities with higher precision!
Example 3: Separation of position isomer compounds fails to work well.
Achieve separation using i-PDeA even though the spectral patterns are similar
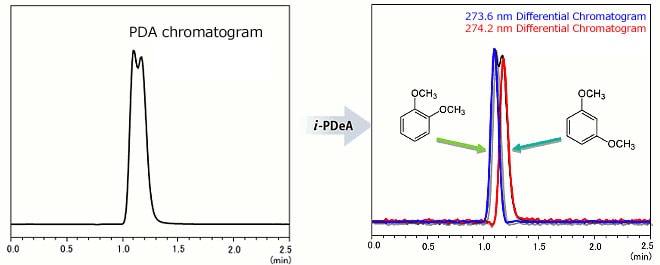
Separation of 1,2-Dimethoxybenzene (274.2 nm wavelength) and 1,3-Dimethoxybenzene (273.6 nm)
Even though the difference in absorption wavelength between 1,2-dimethoxybenzene (274.2 nm wavelength) and 1,3-dimethoxybenzene (273.6 nm) is only 0.6 nm, the individual chromatograms can be obtained!